Nature Methods: Points of Significance
Martin Krzywinski is a staff scientist at Canada’s Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre.
Naomi Altman is a Professor of Statistics at The Pennsylvania State University.
contributing authors
Paul Blainey is an Assistant Professor of Biological Engineering at MIT and Core Member of the Broad Institute.
Danilo Bzdok is an Assistant Professor at the Department of Psychiatry, RWTH Aachen University, Germany, and a Visiting Professor at INRIA/Neurospin Saclay in France.
Kiranmoy Das is a faculty member at the Indian Statistical Institute in Kolkata, India.
Luca Greco is an Assistant Professor of Statistics at the University of Sannio in Benevento, Italy.
Jasleen Grewal is a graduate student in the Jones lab at Canada's Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre.
Anthony Kulesa is a graduate student in the Department of Biological Engineering at MIT.
Jake Lever is a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in Bioengineering at Stanford University in Stanford, California, USA.
Geroge Luta Associate Professor of Biostatistics at the Georgetown University in Washington, DC, USA.
Jorge López Puga is a Professor of Research Methodology at UCAM Universidad Católica de Murcia.
Byran Smucker is an Associate Professor of Statistics at Miami University in Oxford, OH, USA.
Bernhard Voelkl is a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in the Division of Animal Welfare at the Veterinary Public Health Institute, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
Hanno Würbel is a Professor in the Division of Animal Welfare at the Veterinary Public Health Institute, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
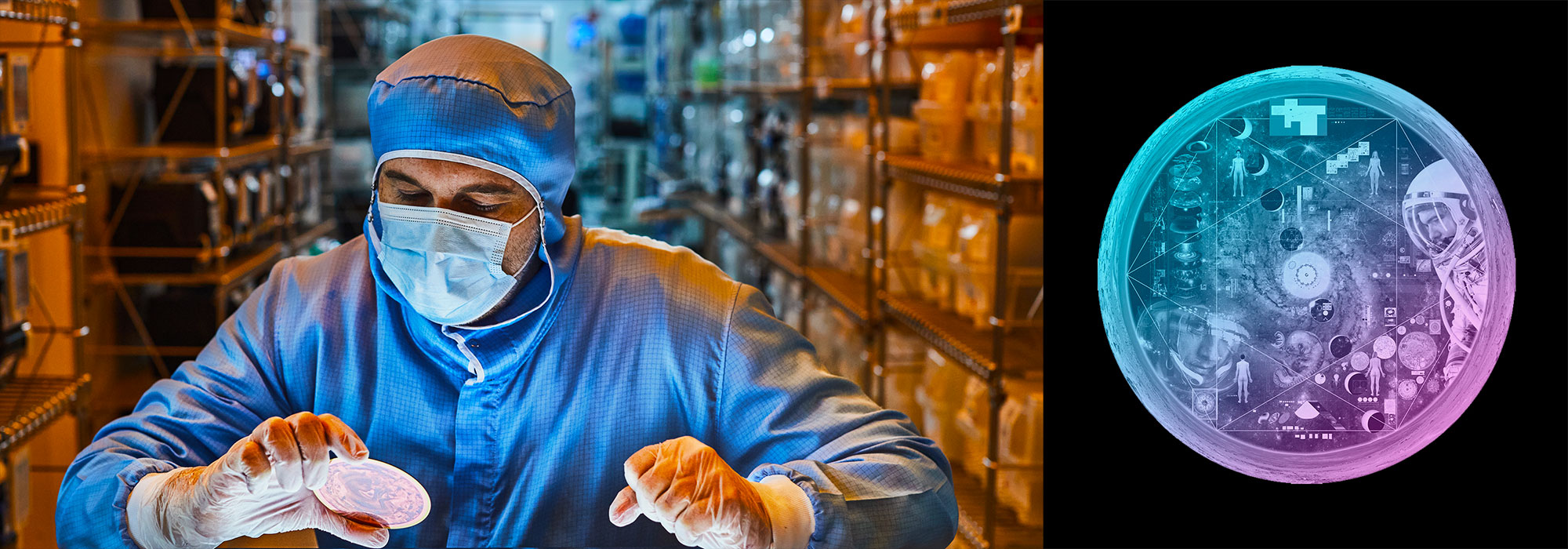
Nasa to send our human genome discs to the Moon
We'd like to say a ‘cosmic hello’: mathematics, culture, palaeontology, art and science, and ... human genomes.



Comparing classifier performance with baselines
All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others. —George Orwell
This month, we will illustrate the importance of establishing a baseline performance level.
Baselines are typically generated independently for each dataset using very simple models. Their role is to set the minimum level of acceptable performance and help with comparing relative improvements in performance of other models.
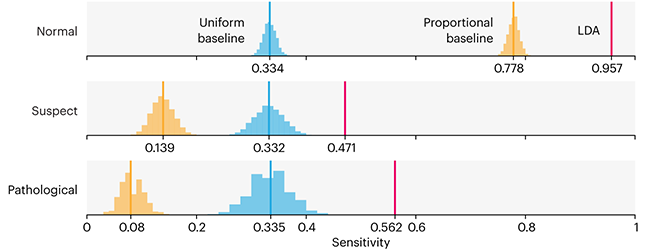
Unfortunately, baselines are often overlooked and, in the presence of a class imbalance5, must be established with care.
Megahed, F.M, Chen, Y-J., Jones-Farmer, A., Rigdon, S.E., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2024) Points of significance: Comparing classifier performance with baselines. Nat. Methods 20.
Happy 2024 π Day—
sunflowers ho!
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and dig into the digit garden. Let's grow something.
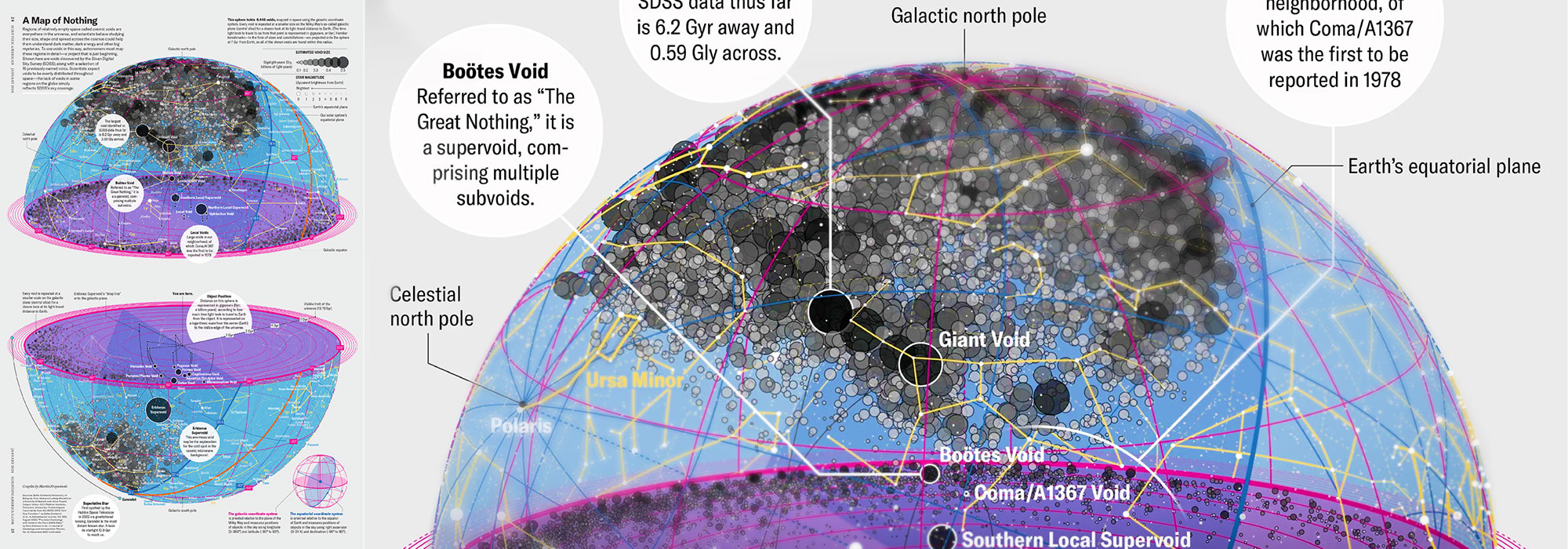
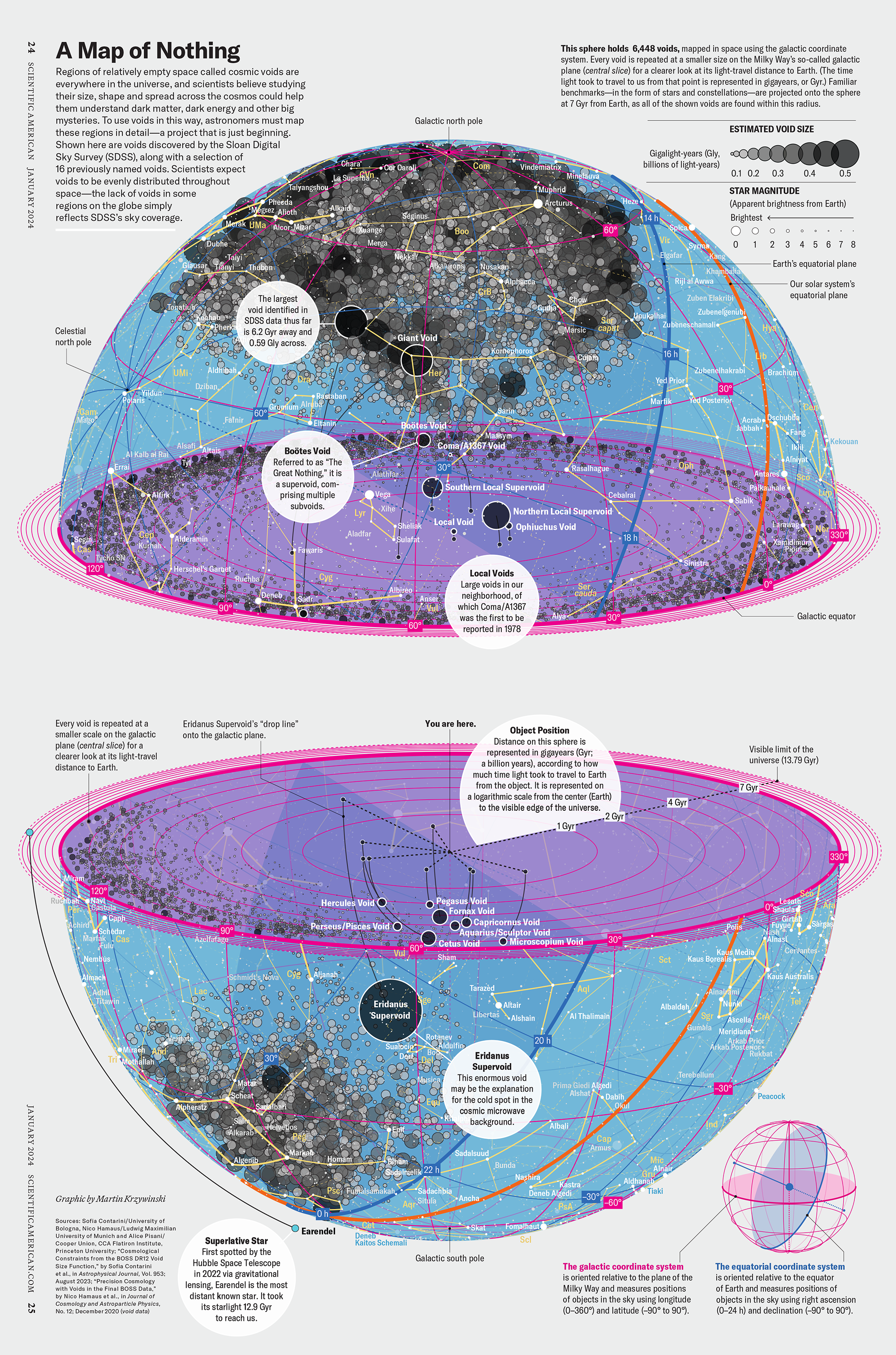
How Analyzing Cosmic Nothing Might Explain Everything
Huge empty areas of the universe called voids could help solve the greatest mysteries in the cosmos.
My graphic accompanying How Analyzing Cosmic Nothing Might Explain Everything in the January 2024 issue of Scientific American depicts the entire Universe in a two-page spread — full of nothing.
The graphic uses the latest data from SDSS 12 and is an update to my Superclusters and Voids poster.
Michael Lemonick (editor) explains on the graphic:
“Regions of relatively empty space called cosmic voids are everywhere in the universe, and scientists believe studying their size, shape and spread across the cosmos could help them understand dark matter, dark energy and other big mysteries.
To use voids in this way, astronomers must map these regions in detail—a project that is just beginning.
Shown here are voids discovered by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), along with a selection of 16 previously named voids. Scientists expect voids to be evenly distributed throughout space—the lack of voids in some regions on the globe simply reflects SDSS’s sky coverage.”
voids
Sofia Contarini, Alice Pisani, Nico Hamaus, Federico Marulli Lauro Moscardini & Marco Baldi (2023) Cosmological Constraints from the BOSS DR12 Void Size Function Astrophysical Journal 953:46.
Nico Hamaus, Alice Pisani, Jin-Ah Choi, Guilhem Lavaux, Benjamin D. Wandelt & Jochen Weller (2020) Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics 2020:023.
Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 12
Alan MacRobert (Sky & Telescope), Paulina Rowicka/Martin Krzywinski (revisions & Microscopium)
Hoffleit & Warren Jr. (1991) The Bright Star Catalog, 5th Revised Edition (Preliminary Version).
H0 = 67.4 km/(Mpc·s), Ωm = 0.315, Ωv = 0.685. Planck collaboration Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters (2018).
constellation figures
stars
cosmology